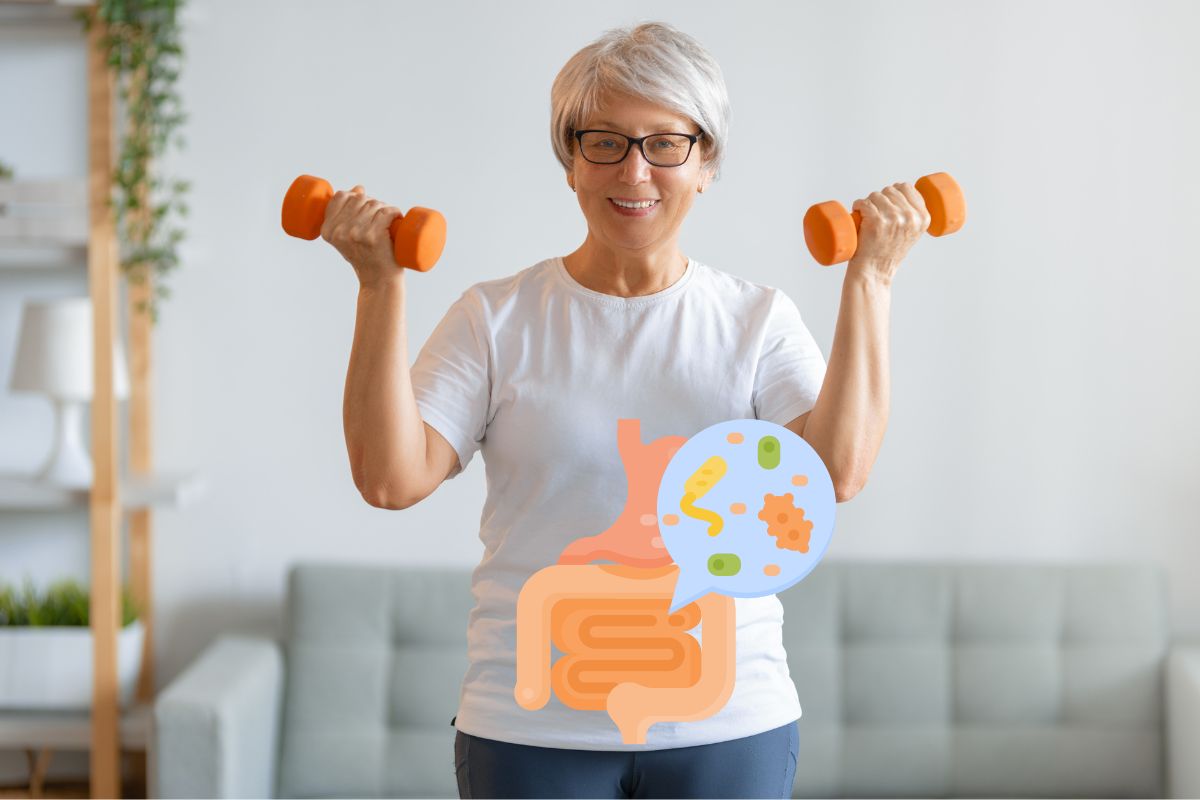
When considering the advantages of exercise, most people think about physical fitness and overall health benefits such as toned muscles, improved cardiovascular function, and weight management. However, there’s an often-overlooked aspect: gut health.
Regular physical activity does more than enhance your physique; it dramatically benefits your digestive system. Exercise positively influences digestion and supports a balanced gut microbiome, which consists of millions of microbes essential for effective digestion.
This article will explore how your workouts, more than you might realize, contribute to optimal digestive health.

The Gut Microbiome: Why It Matters
Understanding the significance of gut health is crucial. Within your digestive system lies an intricate ecosystem of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microorganisms known as the gut microbiome. This diverse community impacts almost every element of your health.
These microbes assist in breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and generating vital vitamins like B12 and K. Beyond digestion, they bolster your immune defense against harmful intruders.
Moreover, the gut is linked to the brain, a relationship termed the gut-brain axis. The health of your gut influences your mood, stress levels, and cognitive abilities. This connection explains why stress often manifests as stomach discomfort.
A balanced gut microbiome is essential for regulating inflammation, aiding digestion, and controlling harmful bacteria. Disruptions can result in digestive problems, lowered immunity, and even mental health issues like anxiety. Thus, maintaining gut health should be prioritized alongside regular exercise.
Exercise and Its Impact on the Gut
The link between exercise and gut health is profound yet subtle. Research highlights that physical movements can significantly affect your digestive system’s function. Exercise enhances microbial diversity and resolves inflammation, each contributing to a healthier gut.

Cardio and Gut Health
Engaging in aerobic activities, such as walking, running, or cycling, is beneficial for your gut. Moderate aerobic exercise promotes bacterial diversity within the gut, strengthening immune responses and improving digestion.
Strength Training and Gut Health
Resistance training, like weight lifting, also promotes gut health by reducing systemic inflammation. This decrease helps protect the gut lining, enhancing nutrient absorption and safeguarding against harmful substances.
High-Intensity Workouts and the Gut
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) boosts beneficial gut bacteria, improving digestion and lowering inflammation. However, it’s crucial to manage recovery properly, as excessive intensity without rest could lead to adverse effects like increased gut permeability.
How Exercise Improves Gut Motility
Gut motility refers to the movement of food throughout the digestive tract. Regular exercise stimulates intestinal muscles, promoting effective movement that helps prevent discomfort, such as bloating and constipation.
Gentle activities, like yoga and walking, can be particularly effective in enhancing gut motility. These activities stimulate the digestive tract and can alleviate symptoms by encouraging regular bowel movements.

Exercise as a Tool for Reducing Gut Inflammation
Chronic gut inflammation can lead to a host of issues, from simple discomfort to serious conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Fortunately, regular physical activity is known for its anti-inflammatory properties.
Exercise encourages the release of anti-inflammatory molecules in the body, bolstering gut health by maintaining the integrity of the gut lining. Consistent, moderate exercise is often most effective at reducing inflammation, fostering a healthy gut environment.

Stress, Exercise, and Gut Health
Stress negatively impacts both the brain and gut. Elevated cortisol levels from stress can disrupt digestion, leading to symptoms like bloating and IBS. Exercise serves as a powerful antidote to stress, releasing endorphins that alleviate anxiety and lower cortisol levels.
Varied forms of exercise can help regulate stress while promoting gut health and motility, creating a harmony between physical activity and digestive function.

Balancing Exercise with Gut Health: Tips for Success
To maximize the benefits of your workouts on gut health, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Start Slow: Gradually ease into exercise, especially if you’re new or returning after a break. Overtraining can stress your gut.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration supports both exercise performance and digestion, so drink plenty of water before, during, and after workouts.
- Combine with a Gut-Friendly Diet: Enhance the benefits of exercise by consuming probiotic-rich foods and fiber to support digestion.
- Rest and Recovery: Prioritize rest and recovery to improve gut health, as adequate sleep and recovery from exercise are crucial.
Boost Your Gut Health and Reduce Inflammation with the 21-Day Fat Loss Challenge
Regular exercise is not just about staying fit; it’s vital for promoting gut health and overall well-being. Whether through cardio, strength training, or everyday activities, making movement a part of your routine profoundly benefits gut health.
For those wanting to elevate their health journey, consider the 21-Day Fat Loss Challenge from Avocadu. This program encourages a healthy diet that complements your exercise routine, emphasizing whole, nutrient-rich foods to enhance gut health and reduce inflammation.

Embrace the opportunity to rejuvenate your diet, improve your gut health, and cultivate a healthier lifestyle. Explore the challenge today and take the first step towards achieving your health goals!

Discover more from Marki Mugan
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.